
For SpaceUpClose.com & RocketSTEM
CAPE CANAVERAL, FL – Gleeful astronomers unveiled an astounding suite of ‘First Light’ imagery captured by NASA’s massive new James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) revealing heretofore unseen vistas of massive cosmic cliffs, star birth in stellar nurseries, star death, evolving and merging galaxies smacking into one another, and detailed spectra of an exoplanet detecting water vapor and so much more at special events at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, Tuesday, July 12 – just a day after President Biden revealed the very first ‘Webb Deep Field’ image peering back further and deeper back in time in our Universe in infrared light than ever before at a White House ceremony, Monday, July 11.
The release of the first set of five science images and spectra is the culmination of more than two decades of work by thousands and thousands of scientists and engineers – and just scratches of surface of the $10 Billion Webb telescopes capabilities.
Webb will observe the gamut of time over billions of years from the current day all the way back to almost the beginning of time and the Big Bang – at objects ranging from nearby planets, stars and exoplanets to the light from the most distant celestial bodies and the formation of the very first galaxies and star formed almost 13.8 Billion years ago.
These first light images represent nothing short of the dawn of a new era in astronomy as the world gets its first look at the full capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope, an international partnership between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).

Webb findings will uncover answers to questions we don’t even know to ask yet says NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
“Today, we present humanity with a groundbreaking new view of the cosmos from the James Webb Space Telescope – a view the world has never seen before,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, at the Goddard event broadcast live on NASA TV.
“These images, including the deepest infrared view of our universe that has ever been taken, show us how Webb will help to uncover the answers to questions we don’t even yet know to ask; questions that will help us better understand our universe and humanity’s place within it.”
“The Webb team’s incredible success is a reflection of what NASA does best. We take dreams and turn them into reality for the benefit of humanity. I can’t wait to see the discoveries that we uncover – the team is just getting started!”
Webb can accomplish all these great things because it has 100 times the resolution of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and six times the light gathering power.
“Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known,” said Nelson quoting famous astronomer Carl Sagan.
“I think these words are becoming reality.”
Webb’s first observations were selected by a group of representatives from NASA, ESA, CSA, and the Space Telescope Science Institute.
The observations were gathered over several months during the telescope commissioning phase that began after the Christmas day 2021 launch and arrived at its final mission destination a million miles (1.6 million km) from Earth.
“From the data I’ve seen so far, from the work we’ve seen in commissioning and then this first week of science, yeah, this is going to be revolutionary,” said Jane Rigby, the Webb operations project manager at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “These are incredible capabilities we’ve never had before.”
Here’s is NASA’s list which also reveals the capabilities of all four of Webb’s state-of-the-art scientific instruments:
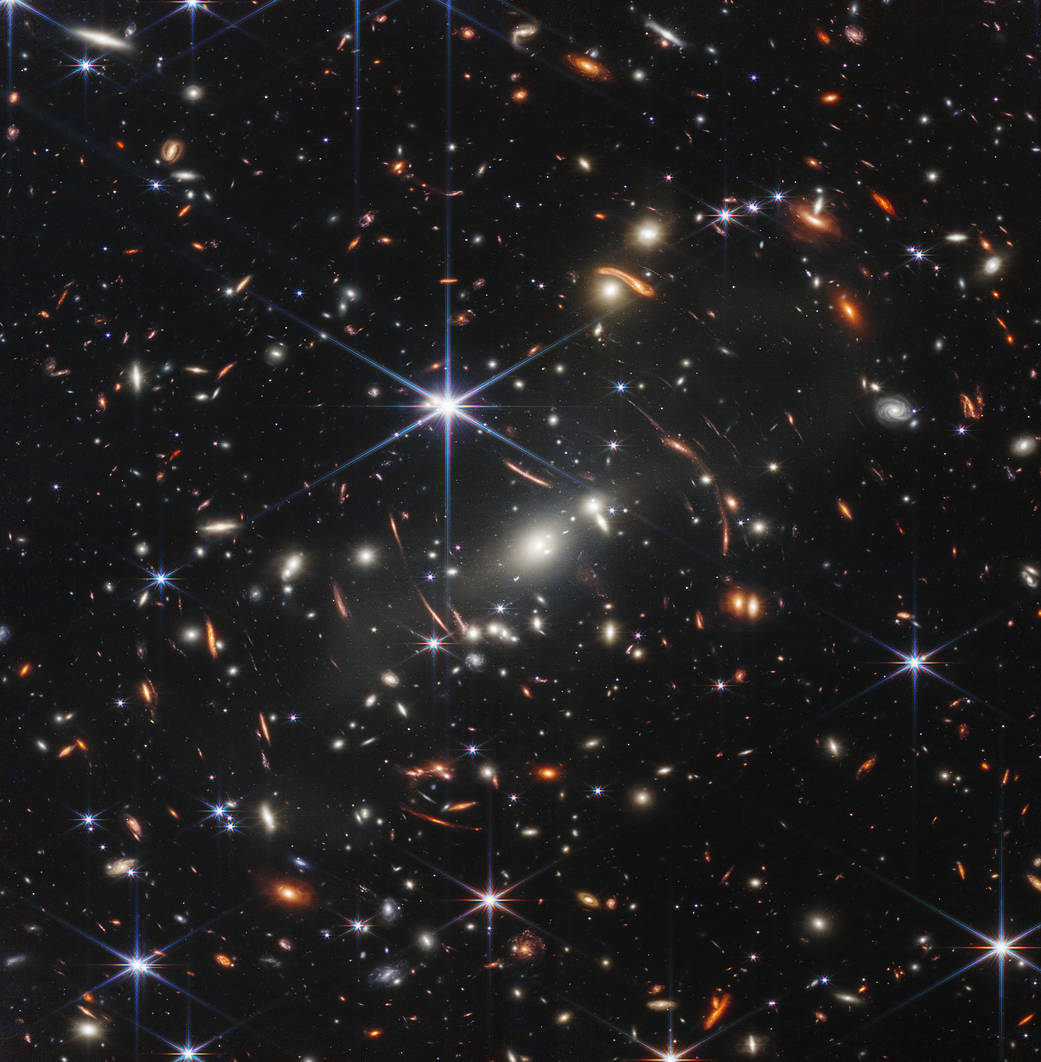
- SMACS 0723: Webb has delivered the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe so far – and in only 12.5 hours. For a person standing on Earth looking up, the field of view for this new image, a color composite of multiple exposures each about two hours long, is approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length. This deep field uses a lensing galaxy cluster to find some of the most distant galaxies ever detected. This image only scratches the surface of Webb’s capabilities in studying deep fields and tracing galaxies back to the beginning of cosmic time.
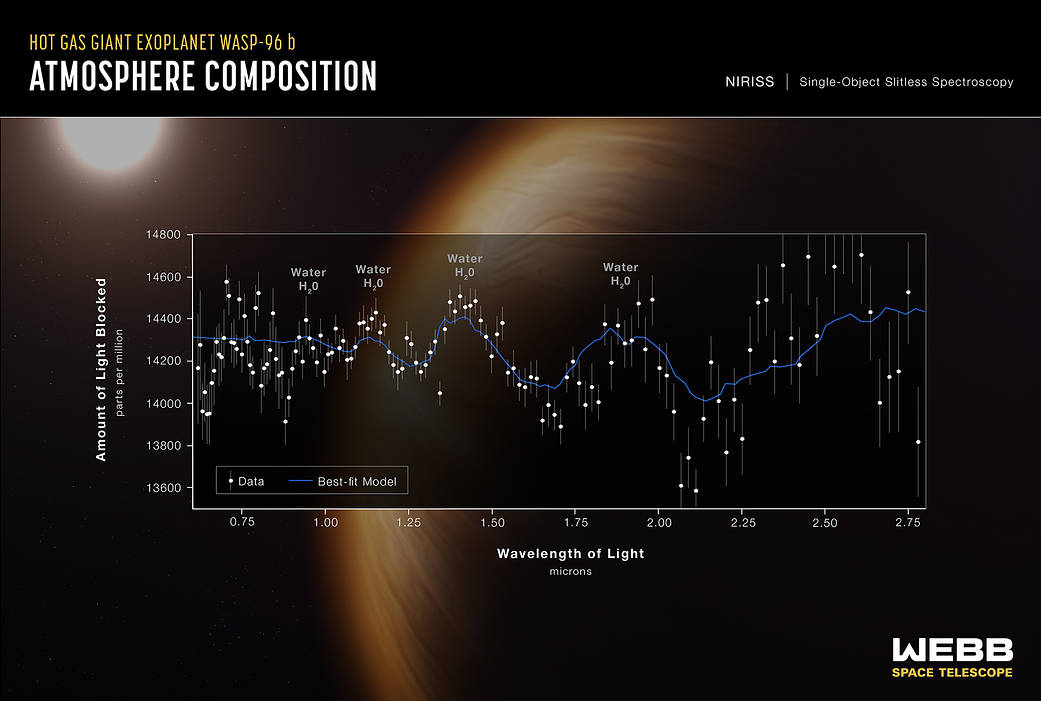
- WASP-96b (spectrum): Webb’s detailed observation of this hot, puffy planet outside our solar system reveals the clear signature of water, along with evidence of haze and clouds that previous studies of this planet did not detect. With Webb’s first detection of water in the atmosphere of an exoplanet, it will now set out to study hundreds of other systems to understand what other planetary atmospheres are made of.
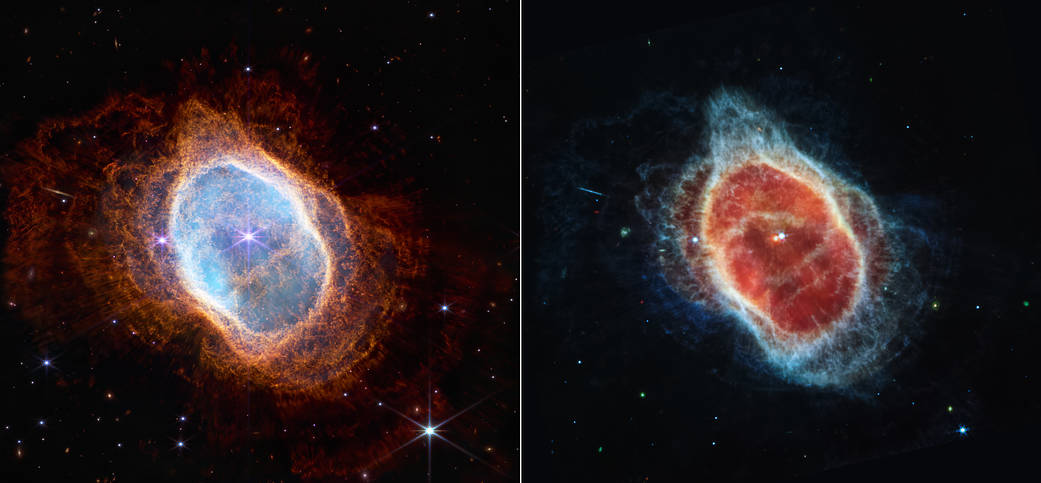
- Southern Ring Nebula: This planetary nebula, an expanding cloud of gas that surrounds a dying star, is approximately 2,000 light years away. Here, Webb’s powerful infrared eyes bring a second dying star into full view for the first time. From birth to death as a planetary nebula, Webb can explore the expelling shells of dust and gas of aging stars that may one day become a new star or planet.
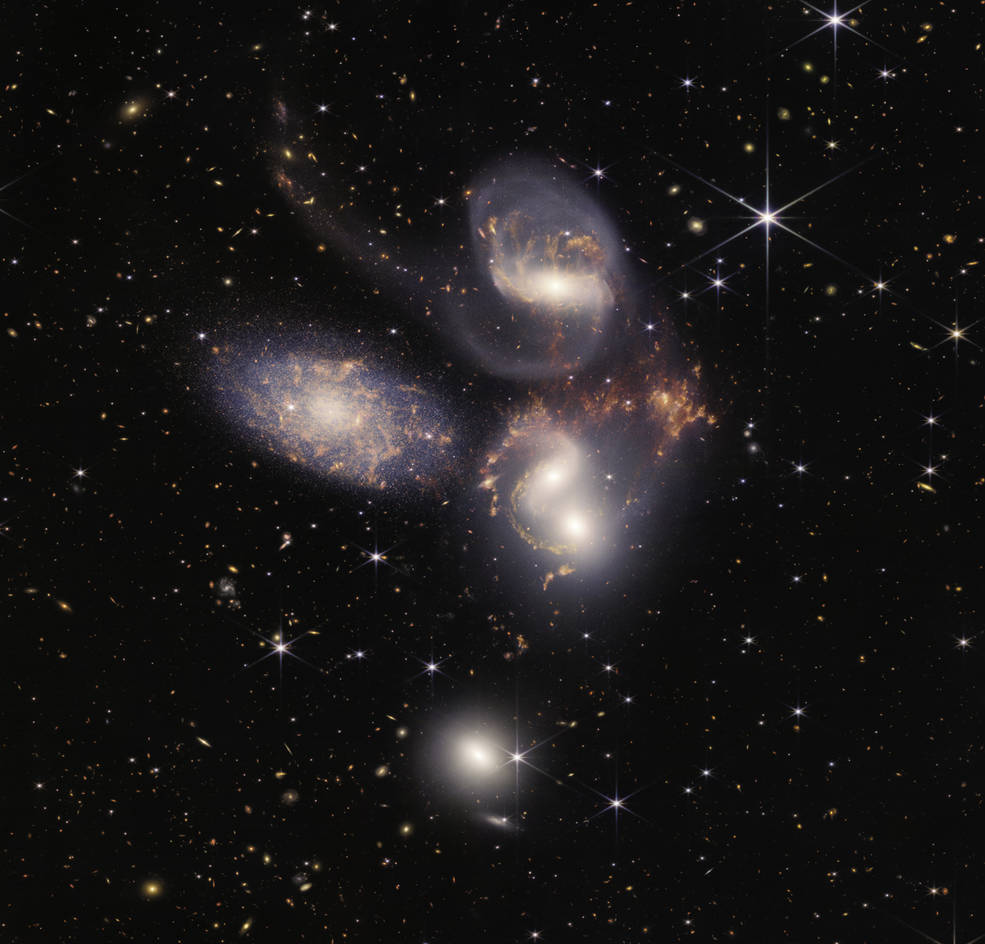
- Stephan’s Quintet: Webb’s view of this compact group of galaxies, located in the constellation Pegasus, pierced through the shroud of dust surrounding the center of one galaxy, to reveal the velocity and composition of the gas near its supermassive black hole. Now, scientists can get a rare look, in unprecedented detail, at how interacting galaxies are triggering star formation in each other and how the gas in these galaxies is being disturbed.
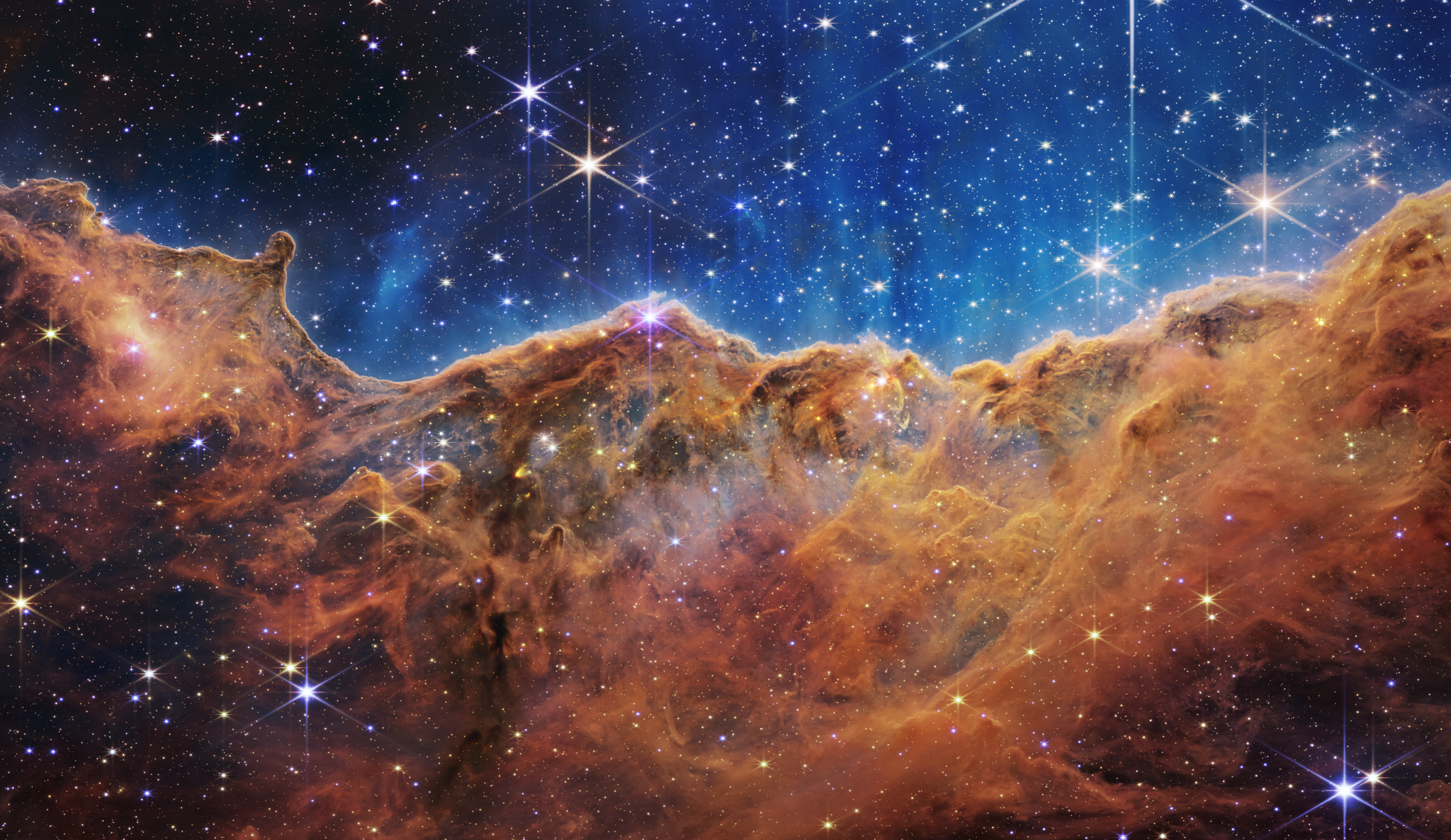
- Carina Nebula: Webb’s look at the ‘Cosmic Cliffs’ in the Carina Nebula unveils the earliest, rapid phases of star formation that were previously hidden. Looking at this star-forming region in the southern constellation Carina, as well as others like it, Webb can see newly forming stars and study the gas and dust that made them.

“Absolutely thrilling!” said John Mather, Webb senior project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “The equipment is working perfectly, and nature is full of surprising beauty. Congratulations and thanks to our worldwide teams that made it possible.”
“I am so thrilled and relieved. We risked so much and its so near impossible. But we did it!”

What are among the top goals?
“What comes after the Big Bang? How did the first stars and galaxies form?” explained Mather during the NASA webcast
On July 11, President Joe Biden unveiled an absolutely stunning first full color science image captured by NASA’s massive new James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) that peers further and deeper back in time in the Universe than ever before and in the highest resolution ever achieved, and showing thousands and thousands of galaxies in unimaginable clarity in the faintest infrared light and dating from the first billion years.
The image known as ‘Webb’s First Deep Field’ showing just a tiny sliver of the Universe as it looked 13 Billion years ago was released by the President during a ceremony held at the White House Monday evening, July 11, with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Vice President Kamela Harris and the Webb team.
“If you held a grain of sand on the tip of your finger at arm’s length, that is the part of the universe that you’re seeing, just one little speck of the universe,” said Bill Nelson, NASA’s administrator, during the White House briefing with President Joe Biden and Vice President Harris.
“And what you’re seeing there are galaxies, you’re seeing galaxies that are shining around other galaxies whose light has been bent, and you’re seeing just a small little portion of the universe.”
“Webb’s First Deep Field is not only the first full-color image from the James Webb Space Telescope, it’s the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe, so far. This image covers a patch of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length. It’s just a tiny sliver of the vast universe,” said Nelson.
Webb is a robotic mission and will function as a cosmic time machine peering back to nearly the beginning of time to see first light and explore the formation of the first stars and galaxies in our Universe in infrared light.
Credits: NASA/Adriana Manrique Gutierrez
The giant school bus sized and nearly 6.8-ton (6.2-metric ton) infrared observatory has huge ambitions – despite being billions over budget and years behind schedule and faced down cancellation from short-sighted budget cutters in Congress.
It seeks to ask and answer the big questions – Who we are? How did we come to be? by looking back to the birth of the Universe
The $9.8 Billion Webb observatory – intricately folded up like origami inside the nose cone – launched at 7:20 a.m. EST (9:20 a.m. GFT / 1220 GMT / 13:20 CET). Saturday, Dec. 25, on a 55 m (180 ft) tall Arianespace Ariane 5 rocket from Europe’s jungle Spaceport at the ELA-3 launch complex in Kourou, French Guiana, on the northeastern coast of South America.
Webb is a joint effort between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
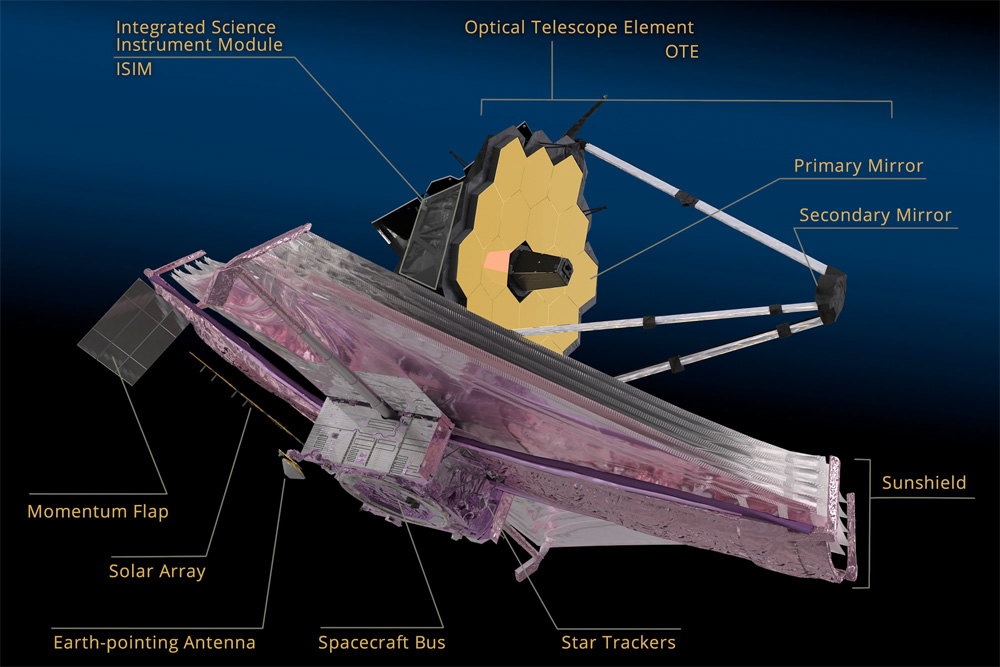
JWST is the largest, most powerful and most complex space telescope ever built.
It is also the most expensive science instrument ever costing nearly $10 Billion
It will operate in a halo orbit at the L2 Lagrange point approx. 1 million miles (1.6 million km) from Earth after liftoff and about a 1-month journey.
It will serve as the scientific successor to NASA’s world famous and phenomenally successful Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
“The James Webb Space Telescope represents the ambition that NASA and our partners maintain to propel us forward into the future,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
“The promise of Webb is not what we know we will discover; it’s what we don’t yet understand or can’t yet fathom about our universe. I can’t wait to see what it uncovers!”
Webb is in many respects a time machine looking back to the formation of the Universe over 13.5 Billion years ago and how we came to be and evolve over the eons.
I observed JWST many times while under construction at NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center in Greenbelt, MD, to observe assembly of the primary and secondary mirrors onto the observatory backbone structure at various points

Watch Ken’s commentary about JWST, Project Artemis, Capstone, NASA SLS WDR demo test, SpaceX missions including NASA Crew-3 and Crew 4, AX-1, Nilesat 301, Transporter-5, Starlink, Boeing Starliner, and NASA TROPICS 1.
Jul 12: Watch Ken’s live interview on NewsNation interview about the release of the stunning first science images taken by NASA Webb and the spectacular discoveries about star birth, star death, galactic evolution, exoplanet atmospheres and much more and what it means.
Watch Ken’s BBC World TV interview about Webb achieving final orbit and the goals ahead on Jan 24, 2022.
Video Caption: Dr. Ken Kremer of Space UpClose live interview on BBC World News TV on Jan. 24, 2022 ET (Jan. 25 GMT) about NASA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) just hours after achieving orbit at its final destination, why at L2, what’s ahead with spacecraft checkouts, what are the science goals and when are first pictures expected
Jul 6/7: Fox 35 Orlando featured my commentary about NASA Capstone cubesat mission – communications just reestablished after 2 day loss. Capstone is a pathfinder mission for NASA’s Gateway mini lunar space station. Now preparing for 1st trajectory correction maneuver (TCM) and heading to lunar orbit
Jul 5/6: WKMG CBS 6 Orlando News featured my commentary about todays loss of contact with NASA’s CAPSTONE lunar cubesat mission. CAPSTONE had been healthy until a 2nd comm pass. Team is attempting to reestablish contact. Goal: test the stability of the unique orbit planned for NASA Gateway mini human space station:
Jul 5/6: WFTV ABC Orlando News featured my commentary about today’s loss of contact with NASA Capstone cubesat mission which is a pathfinder test for the Gateway mini human lunar space station
Jun 21/22: WFTV ABC Orlando News featured my commentary about NASA’s 4th SLS WDR fueling attempt Jun 20, the results and whats ahead after NASA conducts detailed analysis of the 1st tanking test to completely load both stages with LOX & LH2 and run the terminal count to T-29 sec despite a hydrogen leak – achieving many but not all objectives
Jun 17: Fox 35 Orlando featured my commentary about the selection of 2 NASA astronauts to fly on the 1st crewed mission of Boeing Starliner capsule on CFT test flight late 2022 – and what it means for human spaceflight to have a 2nd US commercial crew provider following the successful Boeing Starliner OFT-2 mission for NASA
Jun 9/10: WFTV ABC Orlando features my commentary about the upcoming NASA TROPICS 1 & 2 cubesat science launch on an Astra Rocket 3.3 from pad 46 for NASA which will study the formation and evolution of Tropical Cyclones and Hurricanes. Two more launches will follow for 6 TROPICS cubesats altogether over next few months
Jun 8: WFTV ABC Orlando features my commentary about the SpaceX Falcon 9 launch of NileSat301 telecom sat for Egypt
June 6/7: WFTV ABC Orlando features my commentary about completing 2nd rollout to pad 39B for 2nd round WDR tanking test, what’s involved in and why its critical to the future of Project Artemis:
Watch Ken’s continuing reports about SpaceX missions Artemis, SLS, Orion and NASA missions, SpaceX Crew and Cargo Dragons, SpaceX Axiom-1, JWST, IXPE, DART, Lucy Asteroid mission, GOES, SpaceX Starlink, Commercial Crew and Starliner and Crew Dragon, Blue Origin and Space Tourism, and onsite for live reporting of upcoming and recent SpaceX and ULA launches including Crew 1 & 2 & 3 & 4, ISS, Solar Orbiter, Mars 2020 Perseverance and Curiosity rovers, NRO spysats and national security missions and more at the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news: www.kenkremer.com –www.spaceupclose.com – twitter @ken_kremer – email: ken at kenkremer.com
Dr. Kremer is a research scientist and journalist based in the KSC area, active in outreach and interviewed regularly on TV and radio about space topics.
………….
Ken’s photos are for sale and he is available for lectures and outreach events
Please consider supporting Ken’s work by purchasing his photos and/or donating at Patreon
https://www.patreon.com/kenkremer

x



